Exocytosis
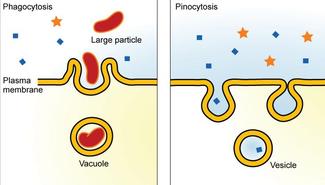
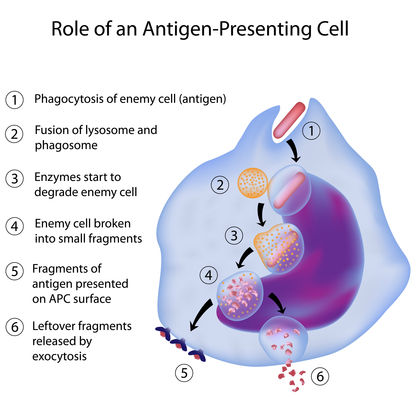
Phagocytosis targets large structures (e.g., bacteria, food particles…) and is not particularly.

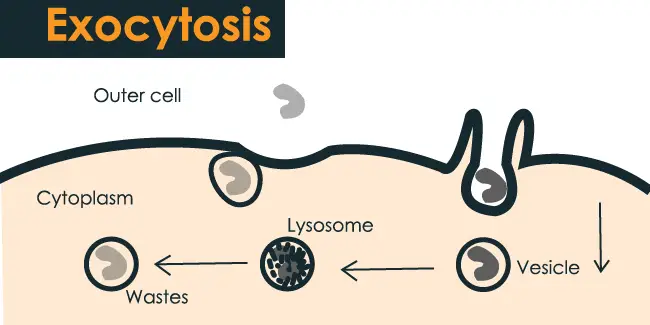
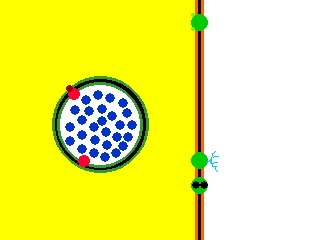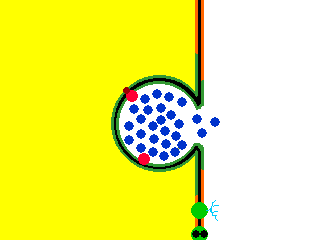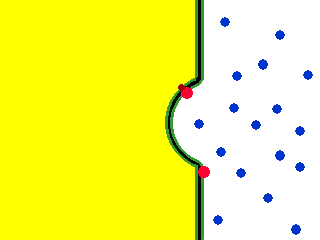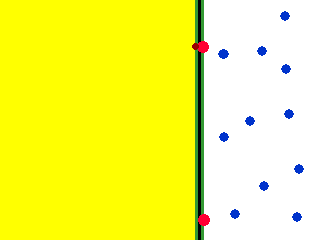
Exocytosis. Exocytosis is a process that uses to move material from inside the cell to the exterior of the cell. Exocytosis serves the following purposes:. Exocytosis (/ ˌɛksoʊsaɪˈtoʊsɪs /) is a form of active transport and bulk transport in which a cell transports molecules (e.g., neurotransmitters and proteins) out of the cell (exo- + cytosis) by secreting them through an energy -dependent process.
Exocytosis is the process of moving materials from within a cell to the exterior of the cell. Therefore, it is a type of active transport mechanism and it is the opposite of endocytosis. Exocytosis provides the opposite function and pushes molecules out of the cell.
The term ‘exocytosis’ was proposed by De Duve in 1963. Exocytosis is a form of active transport that allows cells to move large molecules into the extracellular membrane, where they can be utilized in various ways. As mentioned, this is a form of active transport, rather than passive.
These membrane-bound vesicles contain soluble proteins to be secreted to the extracellular environment, as well as membrane proteins and lipids that are sent to become. Video transcript - Voiceover We have other videos where we talk about how small molecules, or ions, might be able to go through a cell's membrane in different ways, whether actively or passively, maybe facilitated in some way. As compared to endocytosis, exocytosis is a process that is used to transport materials from inside the cell to the external part of the cell by the use of energy.
Like all systems in the human body, the need for homeostasis enables an equal flow of molecules in and out of the cell. Molecules move within the cell or from one cell to another through different strategies. Waste material is enveloped in a membrane and fuses with the interior of the plasma membrane.
Exocytosis is the opposite of the processes discussed in the last section in that its purpose is to expel material from the cell into the extracellular fluid. Phagocytosis, pinocytosis, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Exocytosis is a process that is used to transport materials from inside the cell to the external part of the cell by the use of energy.
This process requires energy and is therefore a type of active transport. (biology) The secretion of substances through cellular membranes, either to excrete waste products or as a regulatory function. Substances internalized by endocytosis include fluids, electrolytes, proteins, and other macromolecules.Endocytosis is also one of the means by which white blood cells of the immune system capture and destroy potential pathogens.
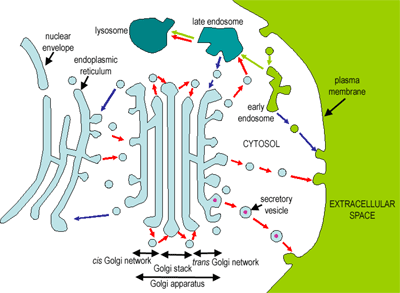
Soluble and secretory proteins leaving the Golgi apparatus undergo exocytosis. In this study, definitions of both terms were request …. Because exocytosis involves fusion between the plasma membrane and the membrane of secretory vesicles, it is likely that proteins on these two membranes, as well as additional proteins in cellular cytoplasm, mediate exocytosis.
Proteins in vesicle are released to the exterior of cell as membrane of the vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane. It explains the difference between endocytosis and exocytosis. Endocytosis definition is - incorporation of substances into a cell by phagocytosis or pinocytosis.
Endocytosis is a mechanism for internalizing large extracellular molecules (e.g., proteins), insoluble particles, or even microorganisms. Many bodily functions include the use of exocytosis, such as the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft and the release of enzymes into the blood. However, both terms have not been uniformly or consistently defined.
Έξω - external and κύτος - cell) is the durable process by which a cell directs secretory vesicles out of the cell membrane. When the exostosis is covered with cartilage, it’s. Exocytosis is important in expulsion of waste materials out of the cell and in the secretion of cellular products such as digestive enzymes or hormones.
The cells inside an organism’s body perform actions like secreting chemicals, releasing energy, expelling wastes, etc. Portable membrane that has cargo embedded in it. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material.
Difference Between Exocytosis And Endocytosis is that The endocytosis is the transport of particles and substances inside the cell, while the exocytosis is intracellular transporting material outward. This process needs energy and therefore is a type of active transport. Exocytosis synonyms, exocytosis pronunciation, exocytosis translation, English dictionary definition of exocytosis.
Exocytosis is the natural process of transporting molecules from within a cell to the outside space. Ex·o·cy·to·ses A process of cellular secretion or excretion in which substances contained in vesicles are discharged from the cell by fusion of the. Endocytosis is the process by which cells internalize substances from their external environment.
- Let's talk a little bit about exocytosis, which is how the cell is able to release larger molecules that might be used by the rest of the body. Exocytosis is the last step of the secretory pathway and it involves the fusion of vesicles with the plasma membrane, a process that, in fungi, ensures the delivery of cell wall-synthesizing enzymes, membrane proteins, and lipids in areas of active growth. The transport of material out of a cell by means of a sac or vesicle that first engulfs the material and then is extruded through an opening in the cell membrane (distinguished from endocytosis).
Exocytosis occurs when a vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane, allowing its contents to be released outside the cell. Transport may be in the form of simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport, osmosis, endocytosis, exocytosis, epithelial transport, or glandular secretion. A process in which a cell releases a large molecule, particle, etc.Origin of exocytosis exo- + cyt(o)- + -osis.
This is a critical process for all living things, from plants and invertebrates to protozoa and human beings. Exocytosis is the opposite of endocytosis as it involves releasing materials from the cell. Examples of how to use “exocytosis” in a sentence from the Cambridge Dictionary Labs.
The secretion of proteins outside the cell is an example of exocytosis. Exocytosis is the process by which cargo-laden transport vesicles move through the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane. Exocytosis is the reverse of endocytosis.
Exocytosis is a process for moving large molecules out of the cell to the cell exterior. Exocytosis is the process by which cells move materials from within the cell into the extracellular fluid. Commonly, these macromolecules originate in storage vacuoles inside the cell and are moved to the exterior after an appropriate signal for this action.
This Biology video tutorial provides a basic introduction into cell transport. Presynaptic nerve terminals release neurotransmitters by synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Endocytosis definition, the transport of solid matter or liquid into a cell by means of a coated vacuole or vesicle (distinguished from exocytosis).
It is how cells get the nutrients they need to grow and develop. The secretion of soluble proteins occurs constitutively. We have moved all content for this concept to for better organization.
These membrane-bound vesicles may contain macromolecules (such as soluble proteins) to be secreted to the extracellular environment, as. In Exocytosis, mainly vesicles built from the Golgi apparatus which contain proteins to dispose of outside the cell and some vesicles contain other waste material. Exocytosis can be constitutive (occurring all the time) or regulated.
Endocytosis includes pinocytosis (cell drinking) and phagocytosis (cell eating). Exocytosis is the process by which a cell packages materials in membrane-bound secretory vesicles inside the cell and directs these secretory vesicles to fuse with the cell membrane (plasma membrane), releasing the packaged materials to the exterior space. Other cells, or maybe it's going to be part of the extracellular matrix.
Process that brings small molecules, macromolecules, large particles, and small cells into a eukaryotic cell. Both processes are due to the need of the cell to maintain with its surroundings an exchange of materials for its survival. In this process, the vesicles containing the fluid enclosed by a lipid bilayer fuse with the plasma membrane to release their contents outside the cell.
What we wanna talk. The release of cellular substances (as secretory products) contained in cell vesicles by fusion of the vesicular membrane with the plasma membrane and subsequent release of the contents to the exterior of the cell Other Words from exocytosis. Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell.
Medical Definition of exocytosis :. Membrane fusion mediating synaptic exocytosis and other intracellular membrane traffic is affected by a universal machinery that includes SNARE (for "soluble NSF-attachment protein receptor") and SM (for "Sec1/Munc …. Exocytosis is the primary means of cellular secretion.
Exocytosis is the cellular process in which intracellular vesicles in the cytoplasm fuse with the plasma membrane and release or "secrete" their contents into the extracellular space. Exocytosis an active process in which vesicles containing excretory or secretory materials are actively carried to the periphery of the cell, and released to the outside when the vesicle membrane fuses with the cell membrane. Describes exocytosis and endocytosis.
Constitutive exocytosis is important in transporting proteins like receptors that function in the plasma membrane. There are three types of endocytosis:. Solid particles within membranes are engulfed by cells.
Molecules move within the cell or from one cell to another through different strategies. The mechanism uses special vesicles fille with the particles of interest to transport Generally, in this mechanism of exocytosis, a special vesicle bound to the cell membrane, containing the cellular particles. This article gives you a brief explanation of these processes and also compares the two.
A segment of the plasma membrane folds inward. There are three exocytosis pathways that deliver vesicles to the plasma membrane. Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes.
Exocytosis is defined as the transport and fusion of secretory vesicles with the plasma membrane and the extracellular space. Transport may be in the form of simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport, osmosis, endocytosis, exocytosis, epithelial transport, or glandular secretion. Exostosis, also called osteoma, is a benign growth of new bone on top of existing bone.
Exocytosis can be constitutive (occurring all the time) or regulated. Uptake of materials from the exterior of the cell. It is the reverse process of endocytosis, in which substances move into the cell.
Once at the plasma membrane, two different things can happen. Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes. It is a form of active transport.
The three main types of exocytosis are phagocytosis, pinocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis.Pinocytosis is non-specific. Endocytosis and exocytosis are used by all cells to transport molecules that cannot pass through the membrane passively. Exocytosis has five stages, each leading up to the vesicle binding with the cell membrane.
It can occur in many parts of the body. Please update your bookmarks accordingly. For these functions, body cells carry out the processes of exocytosis and endocytosis.
The terms 'epidermotropism' and 'exocytosis' are commonly used to describe intraepithelial lymphocytes in the mycosis fungoides (MF) variant of cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL). Exocytosis is an important process of plant and animal cells as it performs the opposite function of endocytosis. In contrast, the exocytosis of secretory proteins is a highly regulated process, in which a ligand must bind to a receptor to trigger vesicle fusion and protein secretion.
Engulfing of bacteria by neutrophils is an example of endocytosis.
Cells Endocytosis Exocytosis Pathwayz

Exocytosis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Lipid Determinants Of Endocytosis And Exocytosis In Budding Yeast Sciencedirect
Exocytosis のギャラリー
Exocytosis Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Function Process System Blood Membrane Molecules

Q Tbn 3aand9gcqmoakgdwtcpbe55rdxdy5pofxy6rsogwrn8q Usqp Cau

Schematic Representation Of Sites Of Exocytosis Or Endocytosis In Download Scientific Diagram

Science Source Endocytosis And Exocytosis Diagram

Exocytosis Wikipedia

Exocytosis Video Membrane Transport Khan Academy

Biodotedu

Endocytosis And Exocytosis Differences And Similarities Technology Networks
Exocytosis Definition Types Steps And Examples 6 27

Real Time Insights Into Regulated Exocytosis Journal Of Cell Science

Active Transport The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

Where Do Lost Membrane Proteins Go After Exocytosis Biology Stack Exchange
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/golgi_exocytosis-5ae36c743de4230037581736.jpg)
A Definition Of Exocytosis With Steps And Examples

Exocytosis And Phagocytosis Youtube

Endocytosis And Exocytosis

Plant Life Endocytosis And Exocytosis
The Cell The Histology Guide
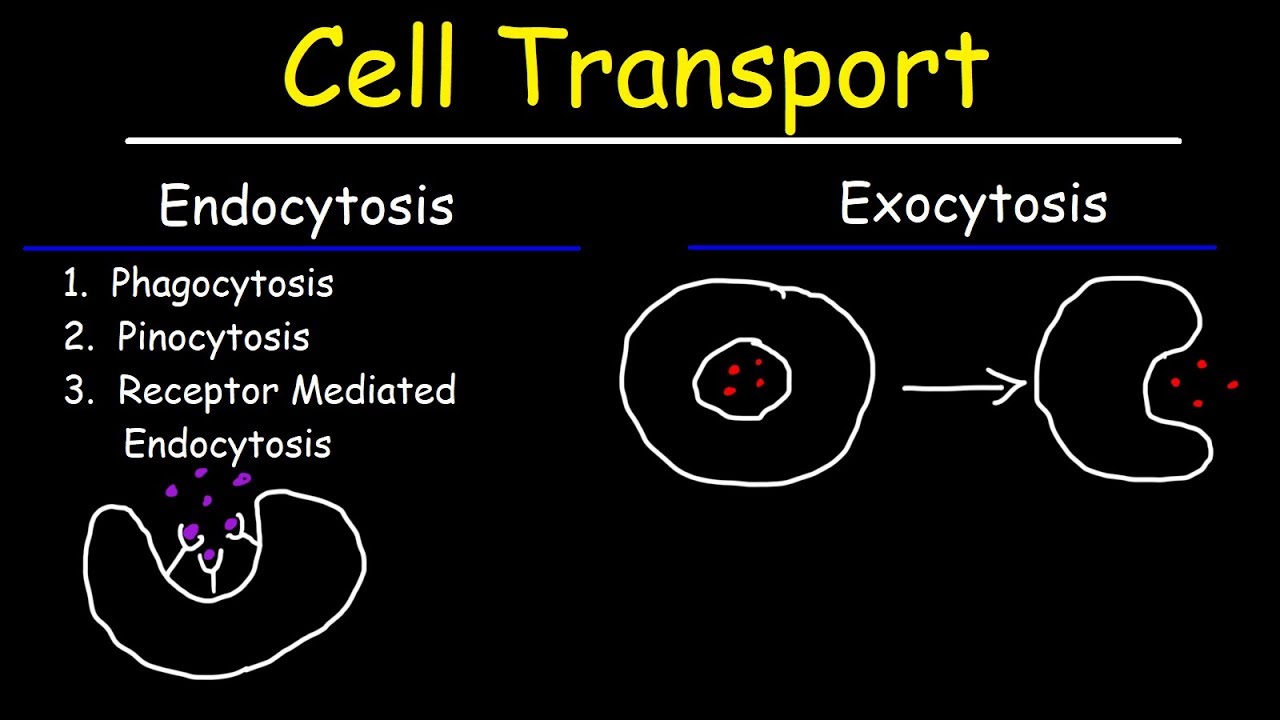
Cell Transport Endocytosis Exocytosis Phagocytosis And Pinocytosis Youtube

Membrane Repair Ca2 Elicited Lysosomal Exocytosis Sciencedirect
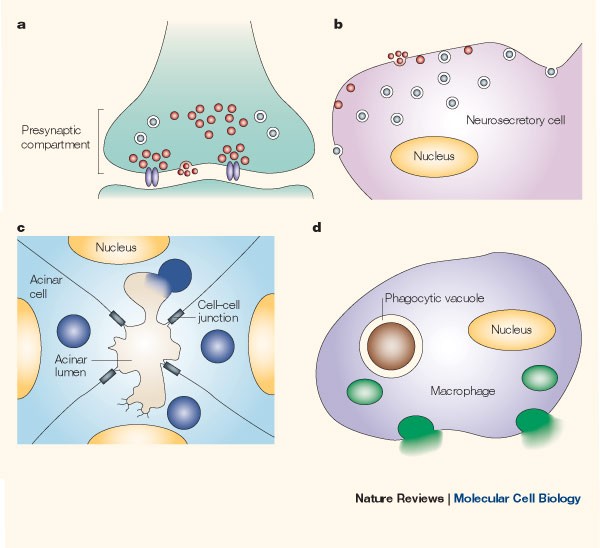
Regulated Exocytosis New Organelles For Non Secretory Purposes Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology

Endocytosis And Exocytosis Differences And Similarities Technology Networks
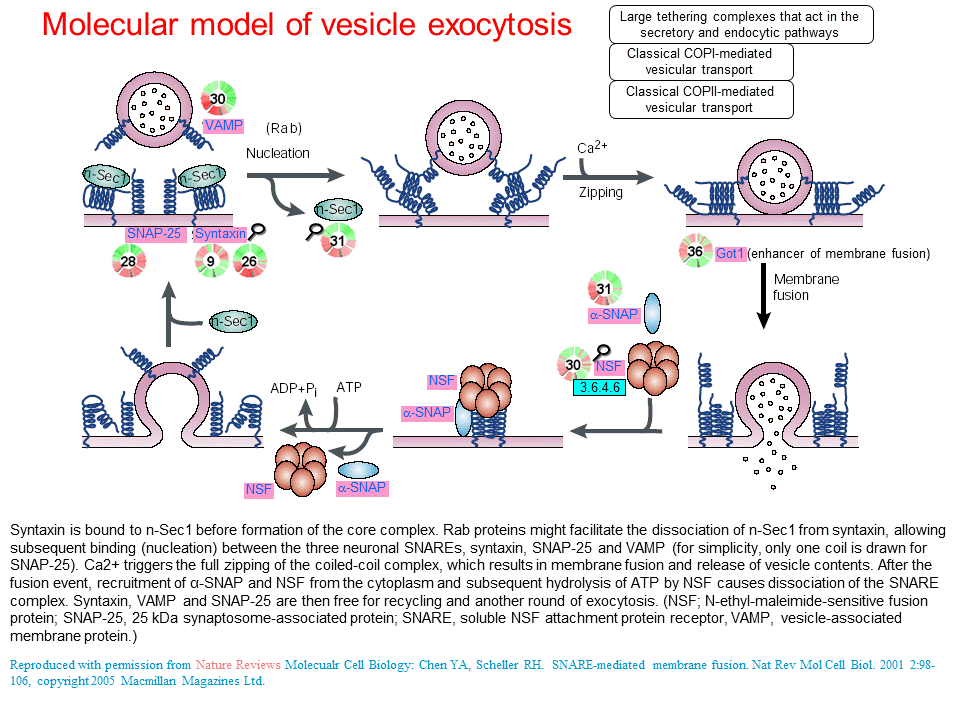
Molecular Model Of Vesicle Exocytosis
Q Tbn 3aand9gcre0ibp3jfn0jeyfg4vek7tsgq2s4qyb7q5zkhxwbs Usqp Cau
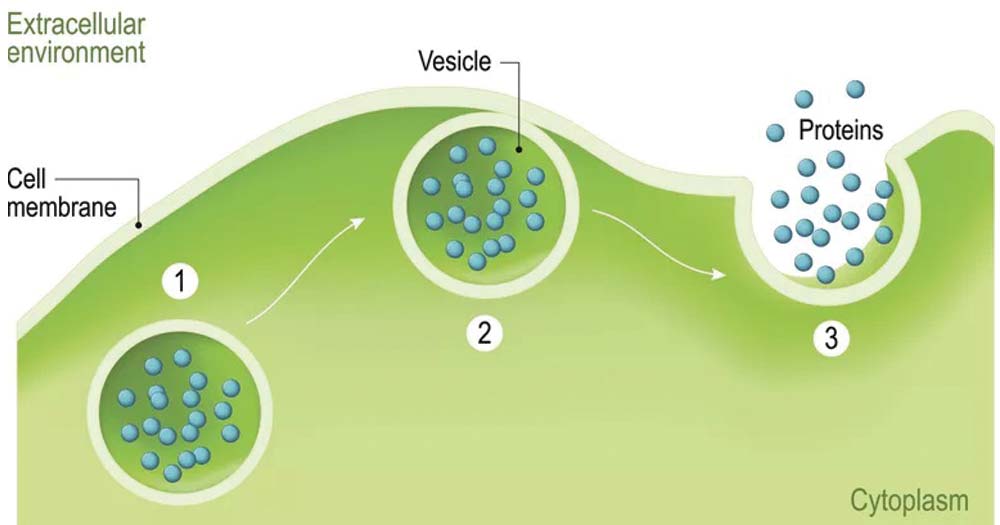
Exocytosis Definition Process And Types With Examples

Actin Remodeling In Regulated Exocytosis Toward A Mesoscopic View Trends In Cell Biology

Exocytosis Also Called Emeiocytosis Or Cell Vomiting Or Reverse Pinocytosis Note It Requires Ca Note Exocytosis Can Be A Constitut การศ กษา

Graphics Gallery An Antibody Molecule
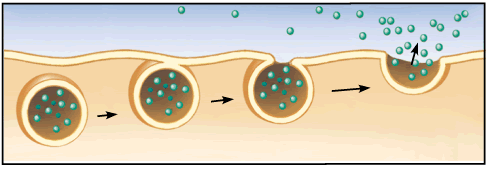
How Do Endocytosis And Exocytosis Maintain Homeostasis Within The Cell Socratic

The Cell 5 Vesicular Trafficking Exocytosis Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology
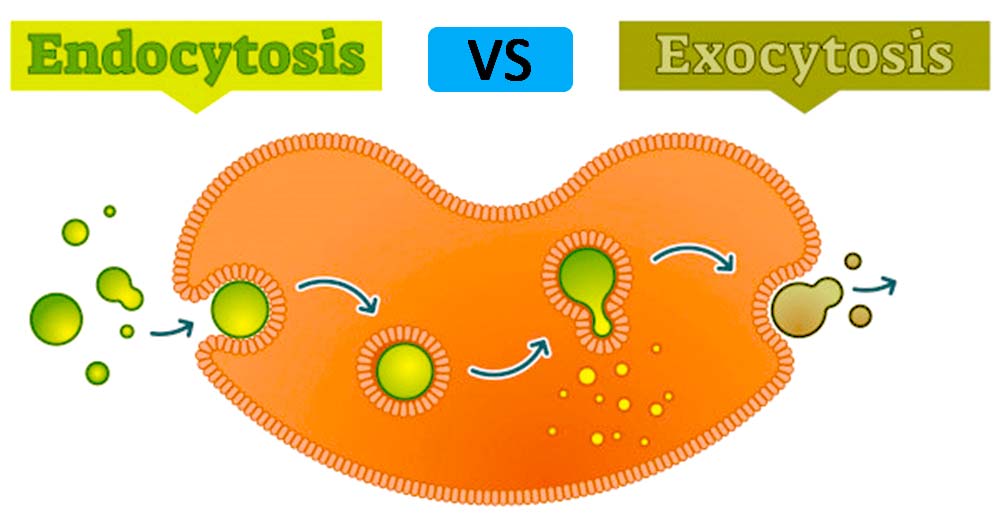
Endocytosis And Exocytosis Endocytosis Vs Exocytosis

Stages Of Exocytosis In Secretory Cells A Formation Of Vesicles B Download Scientific Diagram

Reciprocal Link Between Cell Biomechanics And Exocytosis Wang 18 Traffic Wiley Online Library

Exocytosis Wikipedia
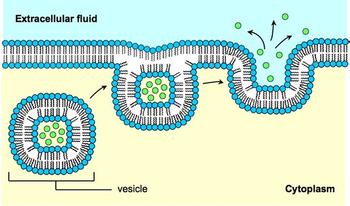
Cells Endocytosis Exocytosis Pathwayz

The Cell 5 Vesicular Trafficking Exocytosis Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology

Exocytosis Secretion Youtube

What Are Endocytosis And Exocytosis Wyzant Resources
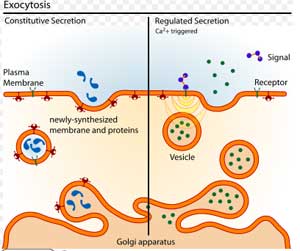
Difference Between Exocytosis And Endocytosis Difference Between
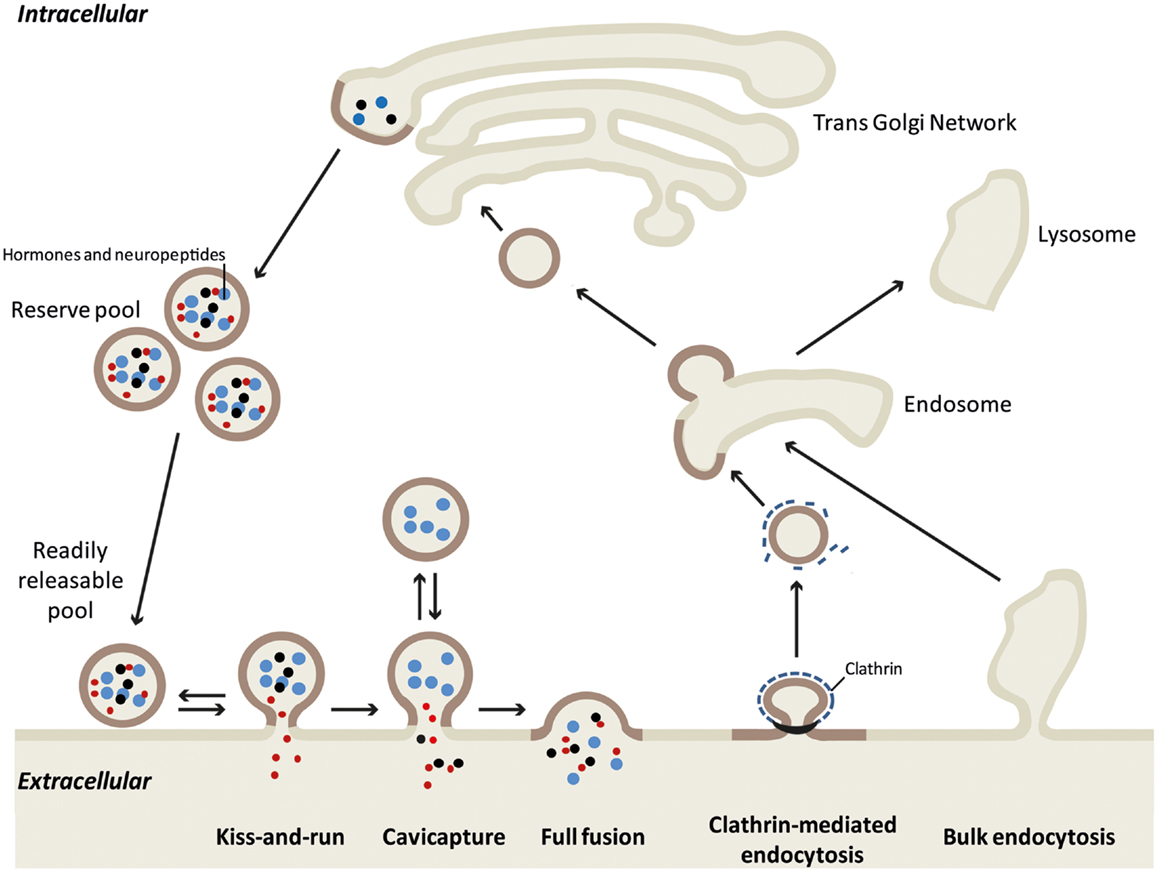
Frontiers Exocytosis And Endocytosis In Neuroendocrine Cells Inseparable Membranes Endocrinology
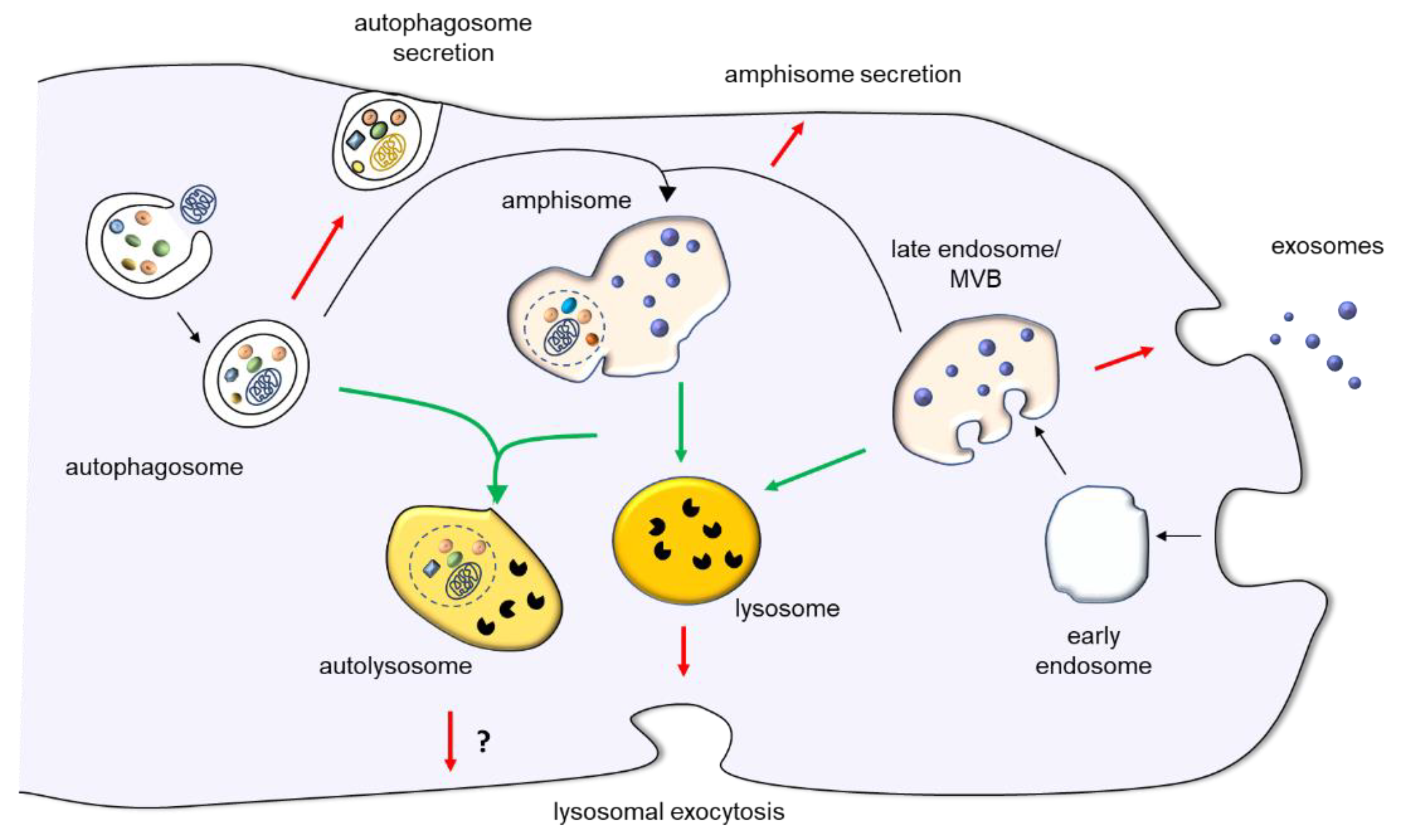
Ijms Free Full Text Lysosomal Exocytosis Exosome Release And Secretory Autophagy The Autophagic And Endo Lysosomal Systems Go Extracellular Html

Exocytosis Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
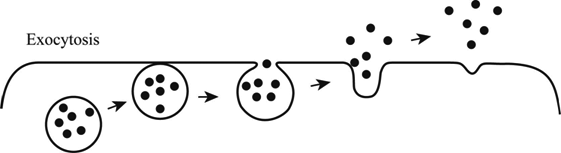
Definition Of Endocytosis And Exocytosis Chegg Com
1
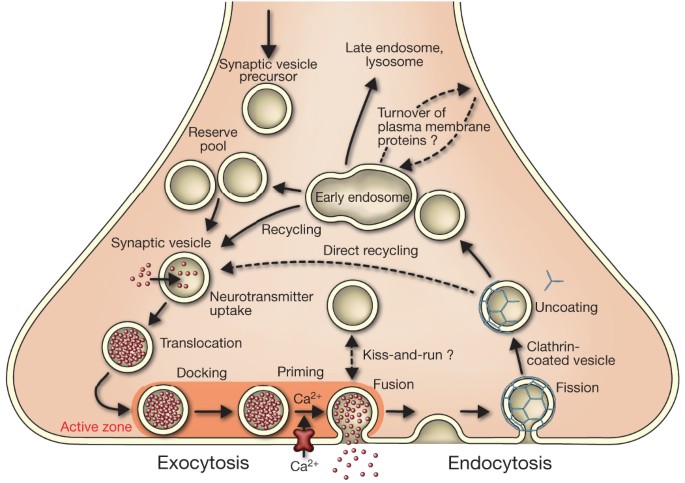
Molecular Machines Governing Exocytosis Of Synaptic Vesicles Nature

Exocytosis All Cells But Especially Important In Secretory Cells Enzymes Hormones Etc And Nerve Cells Ne Cells And Tissues Plasma Membrane Cell Processes
Q Tbn 3aand9gctso9i Xv3k5zw9dgvbplrq149iefdd7fwrrq Usqp Cau
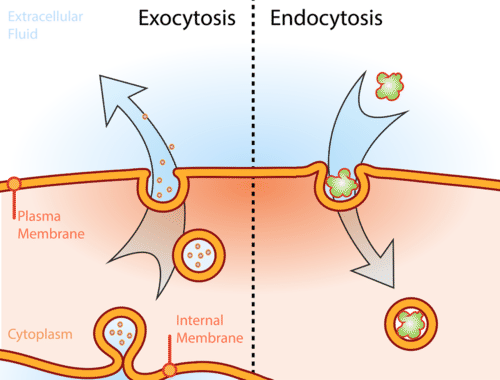
Exocytosis And Endocytosis Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation
Exocytosis Welcome To Biology

Mtrj S Mastermind Cells Endocytosis And Exocytosis

Regulated And Constitutive Exocytosis Of Cytokines Representative Download Scientific Diagram

Exocytosis And Endocytosis Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation

Exocytosis Cell Transports Molecules Out Of The Cell Vesicles Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image

Exocytosis Active Transport Definition Examples Expii
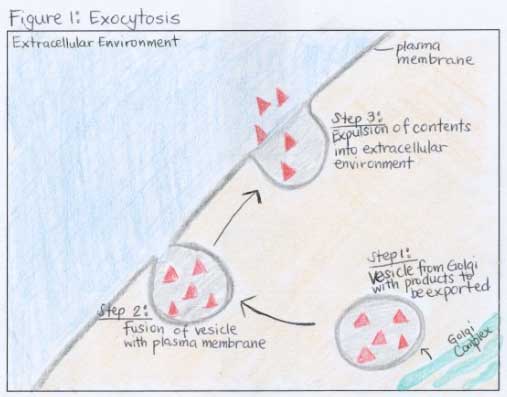
Difference Between Endocytosis And Exocytosis Read Biology

Exocytosis

Calcium Dependent Regulation Of Exocytosis Sciencedirect

The Ins And Outs Of Ige Dependent Mast Cell Exocytosis Trends In Immunology

Endocytosis And Exocytosis Diagram Royalty Free Vector Image
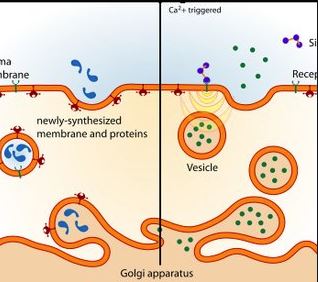
What Are Endocytosis And Exocytosis Wyzant Resources
Q Tbn 3aand9gctvnyuvtfaeug3qlx2asdbf9dzz9qslfvkskpv0rf Xfa7u0xak Usqp Cau

Exocytosis Biology Britannica
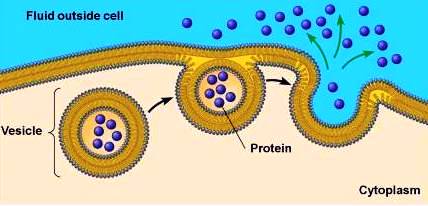
What Is The Relationship Between Endocytosis And Exocytosis Socratic

Exocytosis Biology Britannica

Endocytosis Exocytosis Diagram Diagram Quizlet

Exocytosis And Endocytosis Plant Cell

Lipid Dependent Regulation Of Exocytosis In S Cerevisiae By Osbp Homolog Osh 4 Journal Of Cell Science
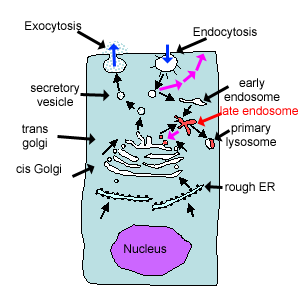
The Cell The Histology Guide

Exocytosis Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock

Intracellular Compartments Exocytosis Endocytosis And The Lysosome Biol230w Fall09 Confluence

Exocytosis Active Transport Definition Examples Expii

What Is Exocytosis Mbinfo

Endocytosis And Exocytosis Differences And Similarities Technology Networks
17 4 Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biology Libretexts
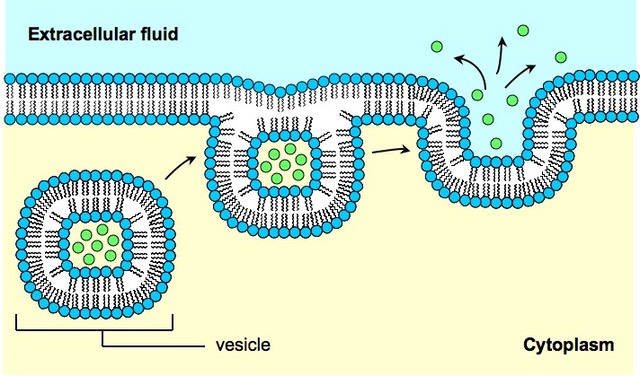
Bulk Transport Bioninja

Neuronal Exocytosis Sciencedirect

Exocytosis Cell Biology Flashcards Draw It To Know It

Schematic Of Endocytosis And Exocytosis Patterns Of Nanoparticles Download Scientific Diagram

Measuring Ca 2 Dependent Lysosomal Exocytosis A Lysosomal Exocytosis Download Scientific Diagram

Exocytosis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Exocytosis Illustration Stock Image C023 8797 Science Photo Library
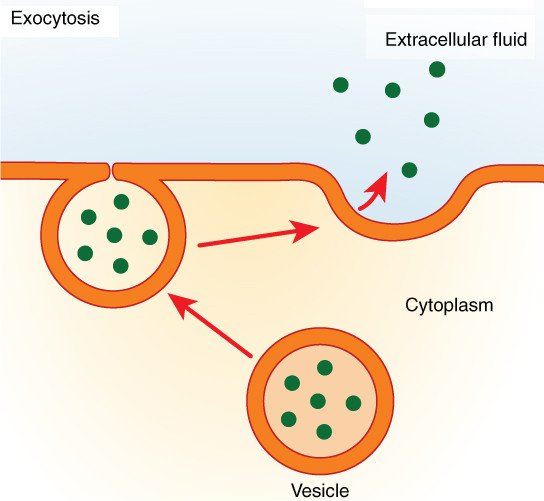
What Is Exocytosis Science Abc

Reciprocal Link Between Cell Biomechanics And Exocytosis Wang 18 Traffic Wiley Online Library
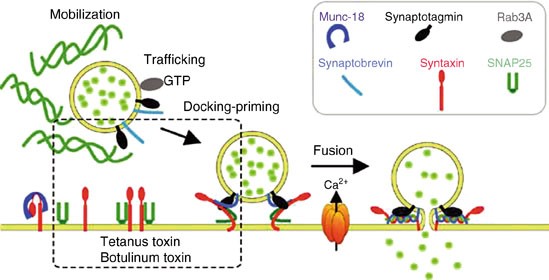
Boipc85njqxfum

Lipids In Regulated Exocytosis What Are They Doing Semantic Scholar
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsshajiw7y7 Gvjeq6oiv7sbfb85znlj7kdnttveknod Hzutjj Usqp Cau

Plant Life Endocytosis And Exocytosis

Exocytosis Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
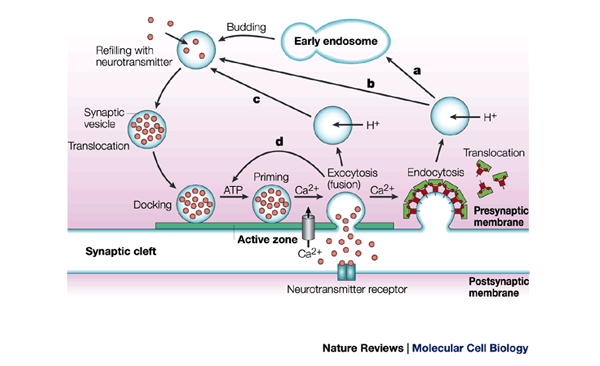
Temporal And Spatial Coordination Of Exocytosis And Endocytosis Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology

Exocytosis Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Endocytosis Exocytosis Autophagy Flashcards Quizlet

Modeling Endocytosis And Exocytosis Perkins Elearning

5 4b Exocytosis Biology Libretexts
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/glucagon_glycogen_glucose-5ae36ebc8023b90036236782.jpg)
A Definition Of Exocytosis With Steps And Examples

Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biology For Majors I
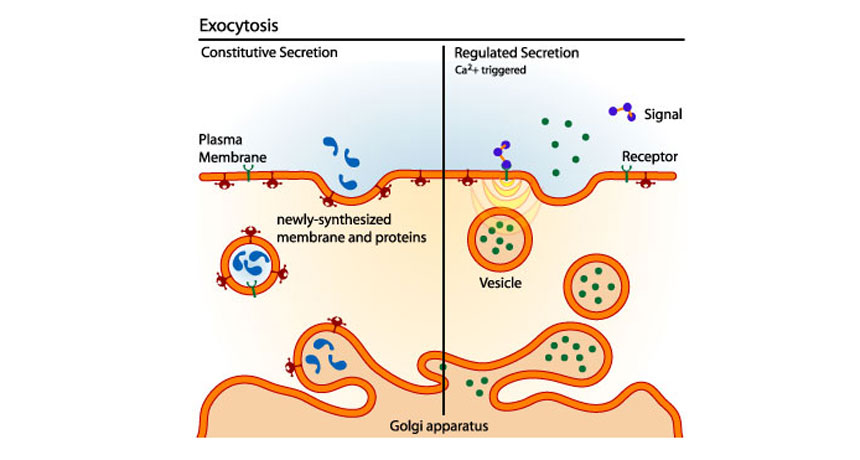
Scientists Say Exocytosis Science News For Students

Different Types Of Exocytosis Endocytosis And Coupling Factors In Download Scientific Diagram

Intracellular Transport 2 4 Exocytosis And The Secretory Pathways Openlearn Open University S377 3

Endocytosis Exocytosis
Endo And Exocytosis Book Chapter Iopscience
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/exocytosis_process-5ae370b4a9d4f900373c9b48.jpg)
A Definition Of Exocytosis With Steps And Examples
Difference Between Endocytosis And Exocytosis Endocytosis Vs Exocytosis



